257. Binary Tree Paths
Given the root of a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths
in any order.
A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1:
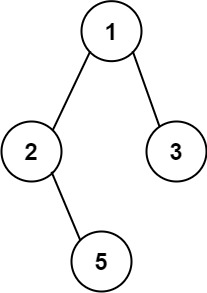
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,5] Output: ["1->2->5","1->3"]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: ["1"]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
program #
class Solution {
List<String> res;
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
//return binaryTreePaths_dfs_iterative(root);
this.res=new ArrayList<String>();
binaryTreePaths_dfs_recursive(root, new StringBuilder());
return this.res;
}
public List<String> binaryTreePaths_dfs_iterative(TreeNode root) {
List<String> out = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null)
return out;
Deque<TreeNode> nodeStack = new ArrayDeque<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
TreeNode pre = null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while(curr != null || !nodeStack.isEmpty()){
if(curr != null){
if(sb.length() > 0){
sb.append("->");
}
sb.append(curr.val);
nodeStack.push(curr);
curr = curr.left;
}else{
curr = nodeStack.peek();
// if leaf node
if(curr.left == null && curr.right == null){
out.add(sb.toString());
}
if(curr.right == null || curr.right == pre){
curr = nodeStack.pop();
int currAppendedStringLength = String.valueOf(curr.val).length();
if(sb.lastIndexOf("->") > -1){
currAppendedStringLength +=2 ;
}
sb.delete(sb.length()-currAppendedStringLength, sb.length());
pre = curr;
curr = null;
}else{
curr= curr.right;
}
}
}
return out;
}
public void binaryTreePaths_dfs_recursive(TreeNode root, StringBuilder pathBuilder) {
if(root == null){
return;
}
if(pathBuilder.length() >= 1){
pathBuilder.append("->");
}
pathBuilder.append(root.val);
binaryTreePaths_dfs_recursive(root.left, new StringBuilder(pathBuilder.toString()));
binaryTreePaths_dfs_recursive(root.right, new StringBuilder(pathBuilder.toString()));
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
this.res.add(pathBuilder.toString());
}
}
}
